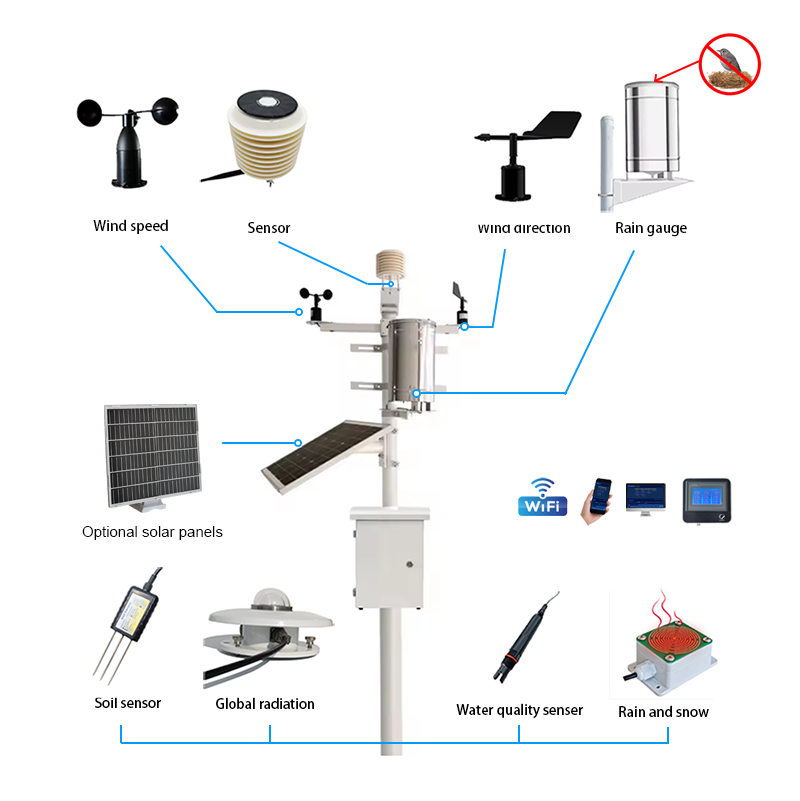
The pole-mounted weather station is a more traditional and standardized meteorological monitoring facility, also known as a traditional discrete weather station or a standard weather station. Its core feature is that sensors with different functions are respectively installed at different heights on one or more vertical poles in accordance with the observation specifications.
The following are the main features of the pole-mounted weather station, which are also elaborated from multiple dimensions:
I. Core Structure and Design Features
1. The sensor is arranged in a discrete layout
This is the most fundamental difference from integrated weather stations. Each sensor (anemometer, wind vane, temperature and humidity sensor, rain gauge, pressure sensor, etc.) is an independent unit and is connected to the main data collector through cables.
The sensor is installed at a specific height on the pole in accordance with its measurement principle and the recommendations of institutions such as the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). For example:
Wind speed and direction sensor: It is usually installed at the highest point (such as 10 meters high) to avoid interference from ground obstacles.
Temperature and humidity sensor: Installed in a louvered box 1.5 meters or 2 meters above the ground to avoid the influence of direct solar radiation and ground reflection.
Rain gauge: Install at 0.7 meters or a specific height, ensuring the opening is level and the surrounding area is open.
Soil temperature and humidity sensors: They are respectively buried in the soil at different depths.
2. The structure is stable and the degree of specialization is high
The poles are usually made of high-strength metals such as stainless steel and galvanized steel, and are equipped with a solid foundation (such as a concrete foundation), which can withstand severe weather conditions like typhoons and heavy snow, ensuring long-term stable operation.
The bracket design is scientific, minimizing interference with sensor measurements as much as possible.
3. Modular design
Each sensor is an independent module that can be calibrated, maintained or replaced independently without affecting the operation of other sensors. This design is very convenient for later maintenance and upgrade.
Ii. Functions and Performance Characteristics
1. It complies with international observation norms and has strong data authority
The layout and installation height of its sensors strictly follow the standards of authoritative institutions such as the WMO. Therefore, the obtained data have high comparability and authority, making it the first choice for national-level meteorological operations, scientific research, and high-precision industrial applications.
2. High measurement accuracy
Because the sensors are discrete, the interference between them can be minimized to the greatest extent (for example, the disturbance of the airflow by the fuselage and the influence of the heat generated by electronic components on temperature measurement).
Higher measurement accuracy can be achieved by using a single sensor with higher performance and greater professionalism.
3. Flexible configuration and strong scalability
Users can flexibly select the type and quantity of sensors according to their specific needs. For instance, it is easy to add radiation sensors, evaporating dishes, ultraviolet sensors, etc.
When new observation elements are needed in the future, it is only necessary to add the corresponding sensors and interfaces on the pole, which has excellent scalability.
4. Professional data acquisition and power supply system
It is usually equipped with a professional data acquisition box, installed on or near the pole, which is responsible for powering all sensors, data collection, storage and transmission.
The power supply system is more powerful and reliable, usually adopting a hybrid mode of mains electricity, solar energy and battery, ensuring continuous operation for a long time even on rainy days.
Iii. Applications and Advantages and Characteristics
It is applied to high-standard and long-term fixed scenarios
National basic meteorological stations/reference stations: The core force for operational operation.
Professional field research: such as ecological research, climate change monitoring, hydrological monitoring, high-precision agricultural meteorology, etc.
Meteorological support for large-scale engineering projects: such as airports, ports, nuclear power plants, and large water conservancy hubs.
Industries that require certified data, such as wind farm power prediction and environmental assessment, can use the data for third-party certification and auditing.
2. The data is long-term continuous and highly reliable
The robust structure and professional lightning protection and anti-corrosion design ensure that continuous and reliable long-term observation sequences can be provided even in unattended harsh environments.
Iv. Potential Limitations
1. The installation is complex, time-consuming and costly
A series of complex procedures such as site investigation, foundation construction, pole erection, precise sensor calibration, and cable laying are required. The installation period usually takes several days or even longer.
The initial investment cost (including equipment, civil construction and installation) is much higher than that of the integrated weather station.
2. Poor portability
Once installed, it is basically a fixed observation and difficult to move. It is not suitable for emergency monitoring or temporary observation tasks that require frequent location changes.
3. Maintenance is relatively complex
Although the modular design is convenient for replacement, maintenance personnel need to climb up the poles or use lifting equipment to maintain the sensors at high places, which poses certain safety risks and operational difficulties.
4. It has high requirements for the installation site
It requires a large area of open space that meets the requirements of observation norms and is difficult to deploy in cities or areas with limited space.
Summary and Comparison
To understand it more clearly, we can make a core comparison between the pole-mounted weather station and the integrated weather station:
| Features | Vertical pole weather Station (split type)
|
Integrated weather station |
| Core structure | The sensors are discrete and installed layer by layer in accordance with the specifications | The sensors are highly integrated into one |
| Precision and Specification | High, in line with international standards such as the WMO | Medium, suitable for commercial and industrial applications |
| Installation and deployment | Complex, time-consuming, costly and requiring professional construction | Simple, fast, plug-and-play, and low-cost |
| Portability | Poor, fixed type | Strong and easy to move |
| Extensibility | It is strong and can flexibly add or delete sensors | Weak, usually a fixed configuration |
| Cost | The initial investment and installation costs are high | The initial investment and deployment costs are low |
| Typical applications | National business stations, research and development, wind farms | Emergency meteorology, smart agriculture, tourist attractions, campus science popularization |
Conclusion
The pole-mounted meteorological station is a “professional player” and “permanent base” in the field of meteorological monitoring. With its high precision, high reliability and compliance with international standards, it serves long-term and fixed observation tasks that have strict requirements for data quality. Integrated weather stations, on the other hand, act as “light cavalry”, winning with their flexibility and convenience, meeting the extensive demand for rapid and low-cost deployment in the Internet of Things era. Both have their own focuses and together they form the modern meteorological observation network.
For more weather station information,
please contact Honde Technology Co., LTD.
WhatsApp: +86-15210548582
Email: info@hondetech.com
Company website: www.hondetechco.com
Post time: Dec-01-2025